Student-centric advice and objective recommendations
Higher education has never been more confusing or expensive. Our goal is to help you navigate the very big decisions related to higher ed with objective information and expert advice. Each piece of content on the site is original, based on extensive research, and reviewed by multiple editors, including a subject matter expert. This ensures that all of our content is up-to-date, useful, accurate, and thorough.
Our reviews and recommendations are based on extensive research, testing, and feedback. We may receive commission from links on our website, but that doesn’t affect our editors’ opinions. Our marketing partners don’t review, approve or endorse our editorial content. It’s accurate to the best of our knowledge when posted. You can find a complete list of our partners here.
Are Scholarships Taxable?
 By
Will Geiger
By
Will Geiger 
Will Geiger is the co-founder of Scholarships360 and has a decade of experience in college admissions and financial aid. He is a former Senior Assistant Director of Admissions at Kenyon College where he personally reviewed 10,000 admissions applications and essays. Will also managed the Kenyon College merit scholarship program and served on the financial aid appeals committee. He has also worked as an Associate Director of College Counseling at a high school in New Haven, Connecticut. Will earned his master’s in education from the University of Pennsylvania and received his undergraduate degree in history from Wake Forest University.
Full BioLearn about our editorial policies

Annie has spent the past 18+ years educating students about college admissions opportunities and coaching them through building a financial aid package. She has worked in college access and college admissions for the Tennessee Higher Education Commission/Tennessee Student Assistance Corporation, Middle Tennessee State University, and Austin Peay State University.
Full BioLearn about our editorial policies

Maria Geiger is Director of Content at Scholarships360. She is a former online educational technology instructor and adjunct writing instructor. In addition to education reform, Maria’s interests include viewpoint diversity, blended/flipped learning, digital communication, and integrating media/web tools into the curriculum to better facilitate student engagement. Maria earned both a B.A. and an M.A. in English Literature from Monmouth University, an M. Ed. in Education from Monmouth University, and a Virtual Online Teaching Certificate (VOLT) from the University of Pennsylvania.
Full BioLearn about our editorial policies

Scholarships are one of the best ways to pay for college. After all, scholarships are essentially free money that never needs to be repaid. But you might be wondering, “Do I have to pay taxes on my scholarships?” Indeed, one of the things that students sometimes do not think about is the impact of scholarships on taxes and whether scholarships are taxable.
It is certainly important to know how both private scholarships and college-specific merit scholarships can impact your federal and state taxes at the end of the year. Generally, scholarships are not taxable income for most students, but exceptions do exist. Keep on reading to learn more about what winning scholarships may mean for your taxes.
Jump ahead to:
- When are scholarships not taxable?
- When are scholarships taxable?
- How do I report scholarships on my taxes if I need to?
- Bottom line for students
When are scholarships not taxable?
Let’s start with the good news: if you are using your scholarship on an accredited institution of education, then they are not taxable. According to the Internal Revenue Service (IRS), scholarships are not taxable under two conditions:
- You’re a candidate for a degree at an educational institution that maintains a regular faculty and curriculum and normally has a regularly enrolled body of students in attendance at the place where it carries on its educational activities,
- The amounts you receive are used to pay for tuition and fees required for enrollment or attendance at the educational institution, or for fees, books, supplies, and equipment required for courses at the educational institution.
Simply, this means that as long as your scholarship is used for educational expenses (tuition, fees, books, or other supplies), you are fine. This scenario represents the vast majority of students.
When are scholarships taxable?
According to the IRS, scholarships are taxable if used for other non-educational purposes (i.e.: you can’t use your scholarship dollars to go on vacation or buy new clothes). This should be pretty obvious for most students.
Interestingly, scholarships can also be taxable if they are used for expenses such as room and board (or housing and food), travel to campus, and equipment that is deemed “optional.” Additionally, stipends earned through teaching, research, or fellowships are considered taxable income (though this will mainly apply to graduate students).
Also, scholarships are taxable if larger than your college’s Cost of Attendance. It’s really hard to get a scholarship larger than the COA, so most of us won’t have to worry about paying taxes on our scholarships. If, however, you are the student who kicks a field goal from mid-field at the half-time of the bowl game for a $500,000 scholarship, more than likely, you will be paying taxes on that scholarship.
Next, we will discuss how you can report your scholarships on your tax forms if you need to.
How do I report scholarships on my taxes if I need to?
The IRS gives students the following guidelines if they do have to pay taxes on their scholarship earnings:
Form 1040 Guidelines
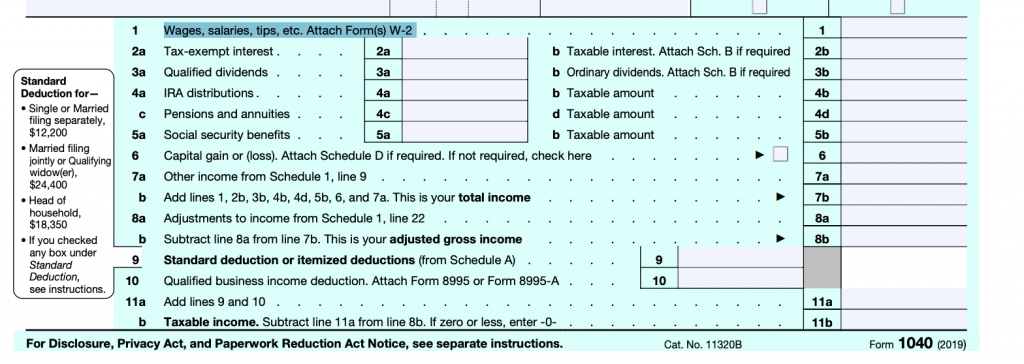
“If filing Form 1040 (PDF) or Form 1040-SR (PDF), include the taxable portion in the total amount reported on the “Wages, salaries, tips” line of your tax return. If the taxable amount wasn’t reported on Form W-2, enter “SCH” along with the taxable amount in the space to the left of the “Wages, salaries, tips” line.“
Form 1040-NR Guidelines
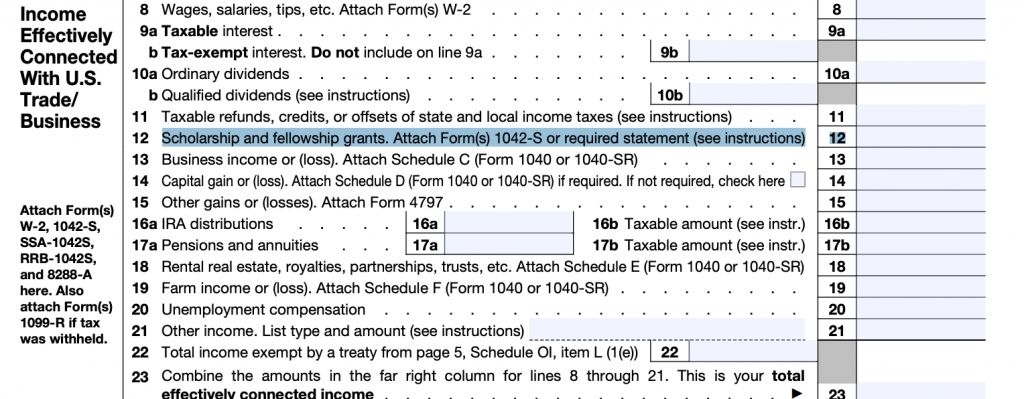
“If filing Form 1040-NR (PDF) or Form 1040-NR-EZ (PDF), report the taxable amount on the “Scholarship and fellowship grants” line.“
Questions about tax forms?
If you have any further questions, we suggest talking to your accountant or financial adviser. Everyone’s situation is different, and a financial professional is going to offer the best information for your situation.
Keep reading:
- Are work study earnings taxed?
- Does financial aid count as income?
- Education tax credits you can earn
- All about the tuition and fees deduction
Frequently asked questions about whether scholarships are taxable
Are scholarships for online learning programs treated differently for tax purposes?
What happens if I use scholarship funds for non-qualified expenses?



